Carotid endarterectomy, a surgical procedure aimed at removing plaque buildup in the carotid arteries, is a crucial intervention for individuals at risk of stroke. The carotid arteries, located in the neck, supply oxygen-rich blood to the brain. When these arteries become narrowed or blocked due to atherosclerosis (plaque buildup), it can lead to a stroke – a potentially life-threatening event. In this edition of Know Your Heart series, we will explore carotid endarterectomy, its significance, and its role in preventing strokes.
Understanding AtherosclerosisBefore understanding carotid endarterectomy, it is essential to grasp the underlying problem: atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is a condition characterized by the gradual accumulation of fatty deposits (plaque) inside the arteries. Over time, these plaques can harden and narrow the arteries, reducing blood flow to vital organs like the heart and brain.
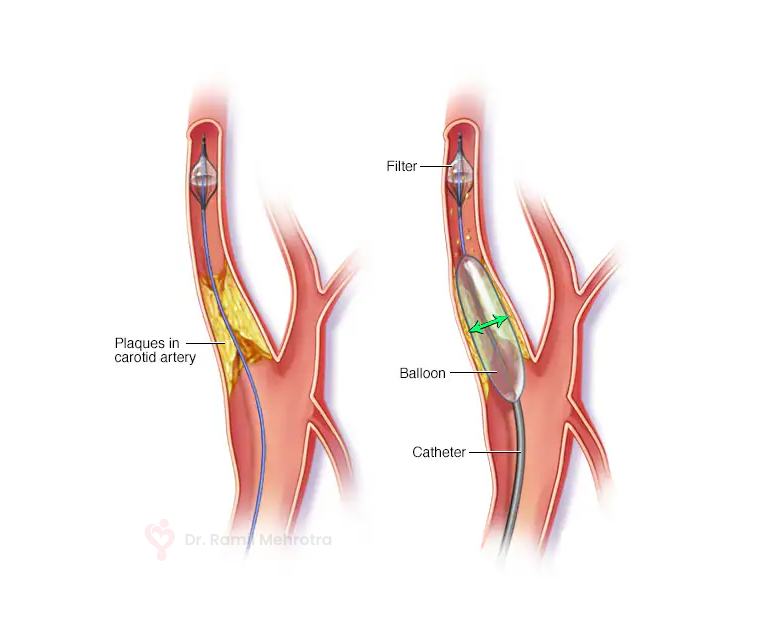
In the case of the carotid arteries, atherosclerosis can lead to carotid artery stenosis. When plaque buildup becomes significant, it narrows the carotid arteries and increases the risk of blood clots forming. If a blood clot breaks loose and travels to the brain, it can block a smaller artery there, leading to an ischemic stroke, which accounts for the majority of strokes.
The Role of Carotid EndarterectomyCarotid endarterectomy is a surgical procedure designed to remove the plaque from the carotid arteries, restoring proper blood flow to the brain. The procedure is typically recommended for individuals with significant carotid artery stenosis who are at high risk of stroke. Following is the step-by-step procedure:
- 1. Anesthesia:The patient is administered either local or general anesthesia to ensure they are comfortable and pain-free during the procedure.
- 2. Incision:The surgeon makes a small incision in the neck, usually along the front edge of the affected carotid artery.
- 3. Artery Access:The surgeon carefully opens the carotid artery to expose the plaque buildup.
- 4. Plaque Removal:Using specialized instruments, the surgeon removes the plaque deposits from the inner lining of the artery.
- 5. Closure:Once the plaque is removed, the surgeon closes the artery with sutures and may use a patch to reinforce the artery’s structure.
- 6. Recovery:After the procedure, the patient is carefully monitored and may need to stay in the hospital for a short period.
Carotid endarterectomy offers several benefits, the most significant being stroke prevention. By restoring proper blood flow to the brain, the procedure significantly reduces the risk of ischemic strokes in patients with severe carotid artery stenosis. Studies have shown that carotid endarterectomy can be highly effective in preventing strokes in the right candidates.
ConclusionCarotid endarterectomy is a vital surgical procedure aimed at preventing strokes in individuals with significant carotid artery stenosis. By removing plaque buildup and restoring proper blood flow to the brain, this procedure can be a lifesaver for those at high risk of stroke.
