The human heart is a complex organ that is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. It is composed of four chambers, each with its own purpose and function. The heart’s valves play a critical role in ensuring the proper circulation of blood through the heart and the rest of the body.
In this edition of the Know your Heart Series, we will discuss the heart’s valves and their importance in maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system.
The Four ValvesThe heart has four valves, which are the mitral valve, the tricuspid valve, the aortic valve, and the pulmonary valve. These valves are located between the heart’s chambers and are responsible for controlling the flow of blood in and out of each chamber.
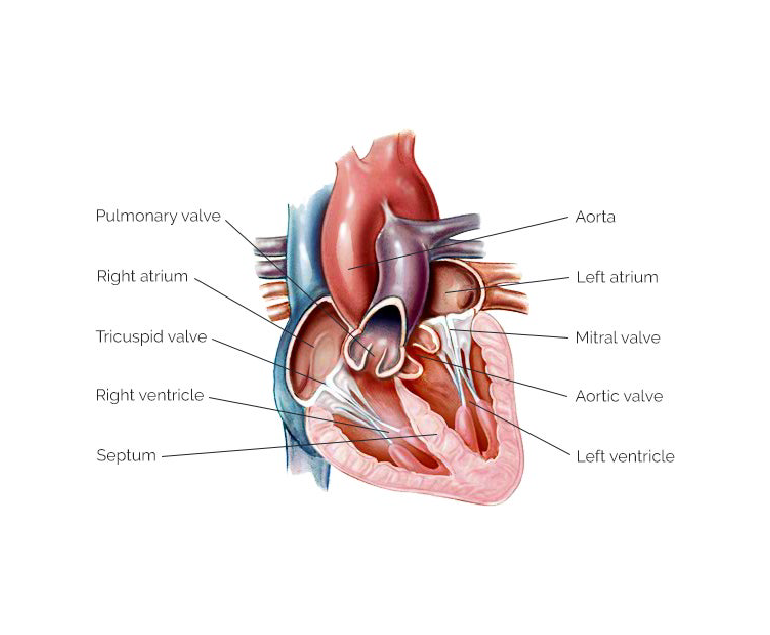
The mitral valve and the tricuspid valve are located between the atria and the ventricles of the heart. The mitral valve is located between the left atrium and left ventricle, while the tricuspid valve is located between the right atrium and right ventricle. These valves are responsible for preventing the backflow of blood into the atria when the ventricles contract to pump blood out to the rest of the body.
The aortic valve and the pulmonary valve are located between the ventricles and the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart. The aortic valve is located between the left ventricle and the aorta, which is the largest artery in the body. The pulmonary valve is located between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery, which carries blood to the lungs to pick up oxygen. These valves are responsible for preventing the backflow of blood into the ventricles when they relax between contractions.
The heart’s valves are made up of strong, fibrous tissue called collagen. The valves also contain a thin layer of endothelial cells, which line the interior surface of the heart and blood vessels. The endothelial cells help to prevent the formation of blood clots and other types of cardiovascular disease.
Conditions affecting valvesWhen the heart’s valves function properly, they allow for the smooth and efficient flow of blood through the heart and the rest of the body. However, when the valves do not work properly, it can lead to a variety of cardiovascular conditions.
One common condition that affects the heart’s valves is called valvular stenosis. Valvular stenosis occurs when the valve opening narrows, making it more difficult for blood to flow through the valve. This condition can cause symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue. It can also lead to complications such as heart failure, stroke, and even sudden cardiac death.
Another condition that affects the heart’s valves is called valvular regurgitation. Valvular regurgitation occurs when the valve does not close properly, causing blood to leak back into the chamber it just left. This condition can also cause symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue. It can also lead to complications such as heart failure and arrhythmias.
In some cases, valvular stenosis or regurgitation can be treated with medications or surgical procedures. In other cases, the valve may need to be replaced with a prosthetic valve.
ConclusionThe heart’s valves are an essential component of the cardiovascular system. They play a critical role in ensuring the proper circulation of blood through the heart and the rest of the body. When the valves function properly, they allow for the smooth and efficient flow of blood. However, when the valves do not work properly, it can lead to a variety of cardiovascular conditions that can have serious consequences. It is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a healthy diet, and avoiding smoking, to help prevent valvular disease and other types of cardiovascular disease.
