Enlarged heart, also known as cardiomegaly, is a condition that occurs when the heart becomes abnormally enlarged, either due to a health condition or as a natural response to stress. Cardiomegaly can lead to a range of serious health problems, including heart failure, arrhythmias, and cardiac arrest.
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of cardiomegaly. These include high blood pressure, coronary artery disease, heart valve disease, congenital heart defects, and viral infections such as myocarditis. Cardiomegaly can also occur in response to lifestyle factors such as obesity, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption.
The symptoms of cardiomegaly can vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. In some cases, individuals with cardiomegaly may not experience any symptoms at all. However, common symptoms of cardiomegaly may include shortness of breath, fatigue, chest pain, dizziness, and palpitations. Severe cases of cardiomegaly may cause fluid build-up in the lungs or legs, leading to swelling and discomfort.
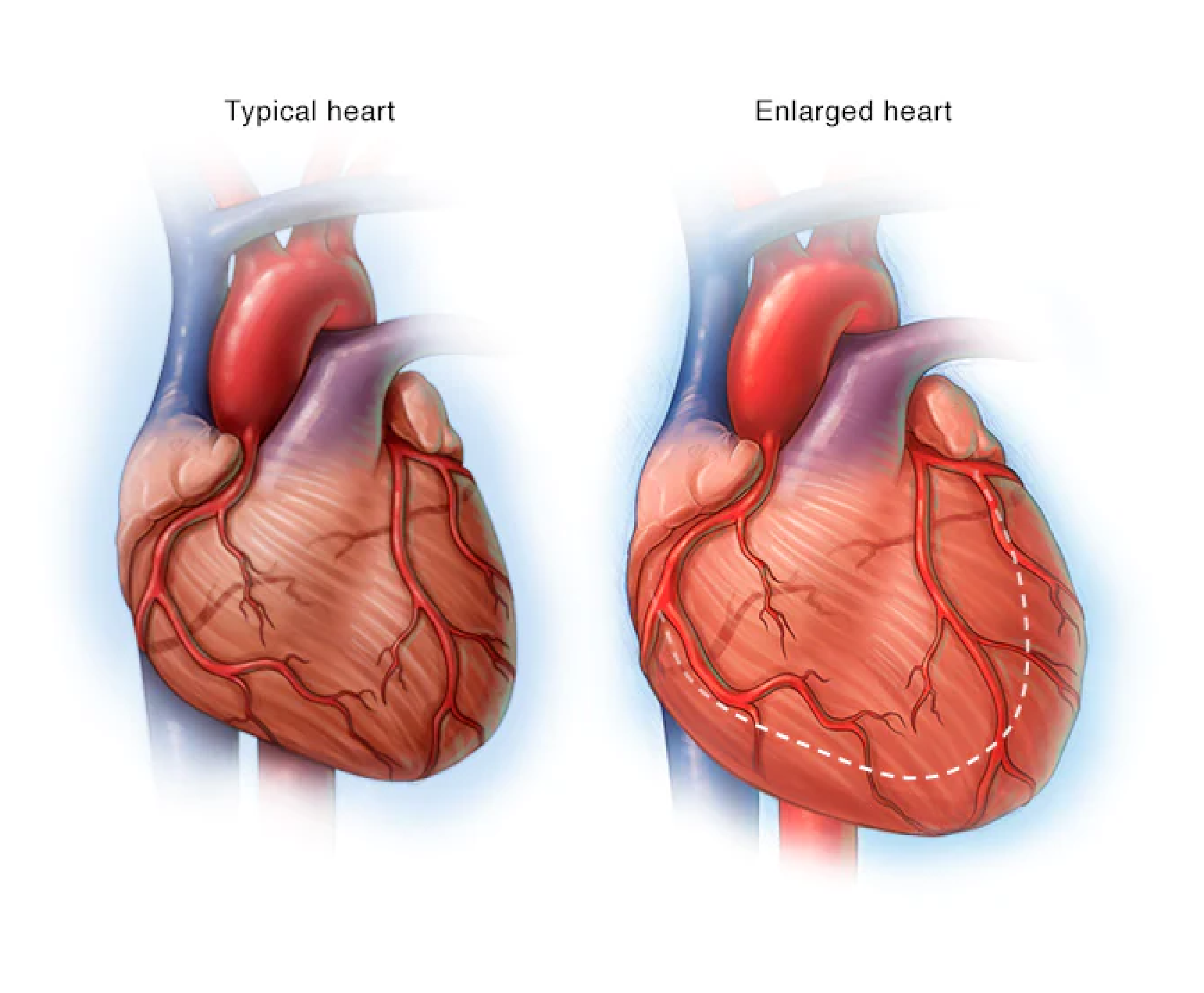
Diagnosis of cardiomegaly typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests such as echocardiography, electrocardiography, and chest X-rays. In some cases, additional tests such as cardiac MRI or cardiac catheterization may be necessary to fully evaluate the condition.
Treatment of cardiomegaly varies depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. In many cases, treatment may involve lifestyle modifications such as weight loss, smoking cessation, and limiting alcohol consumption. Medications such as ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and diuretics may also be prescribed to manage symptoms and reduce the risk of complications.
In severe cases of cardiomegaly, surgery may be necessary to correct the underlying problem. Surgery may involve repairing or replacing heart valves, or removing excess tissue in the heart. In some cases, a heart transplant may be necessary.
Prevention of cardiomegaly involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a healthy diet, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. It is also important to manage any underlying health conditions such as high blood pressure or coronary artery disease.
In conclusion, enlarged heart (cardiomegaly) is a serious condition that can lead to a range of health problems if left untreated. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial for managing the condition and preventing complications. If you experience any symptoms of cardiomegaly, it is important to seek medical attention promptly to ensure the best possible outcome.
