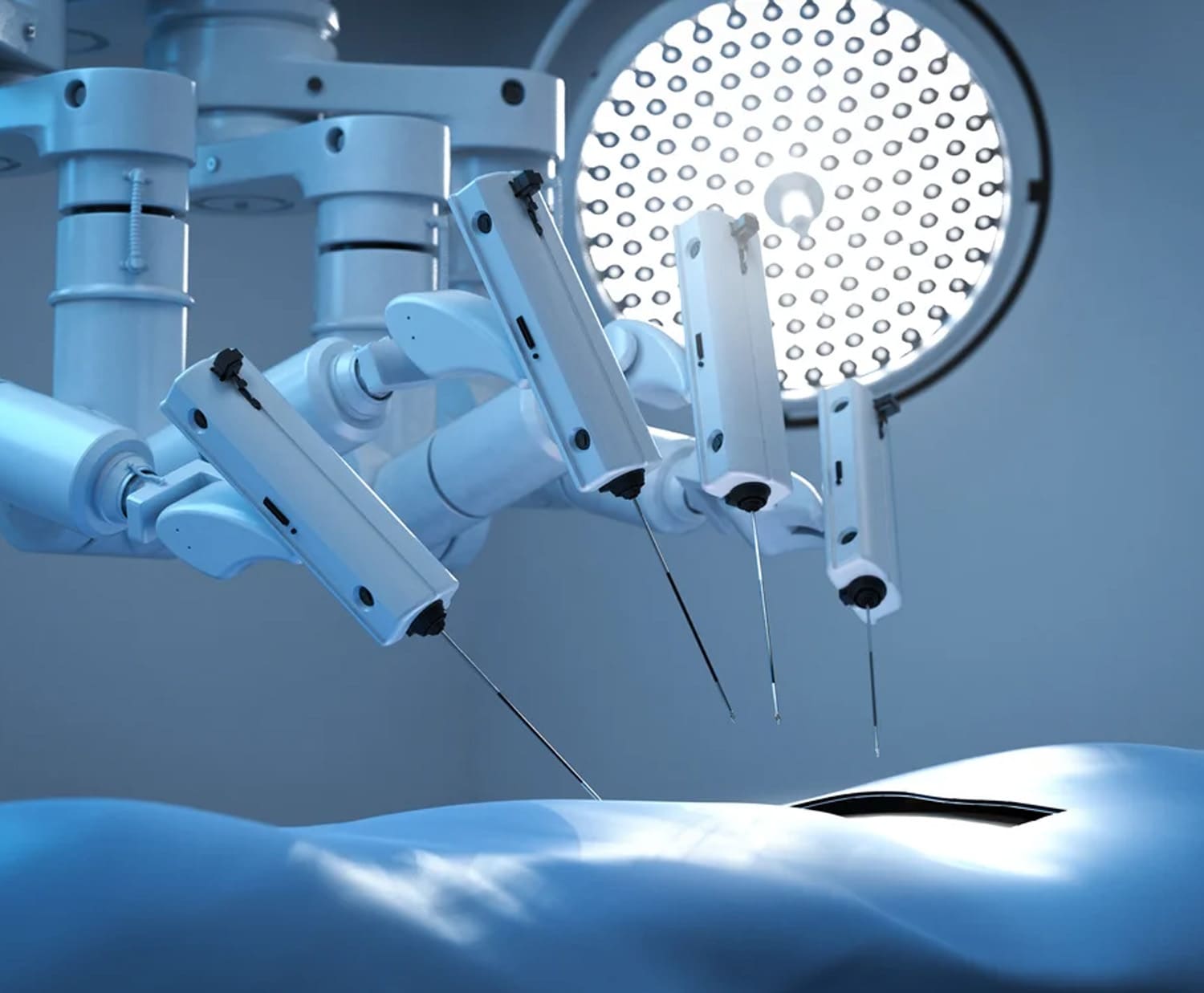
Robotic Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG)
Robotic Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) is a surgical procedure that combines the use of robotic technology with traditional coronary artery bypass grafting techniques. This approach aims to improve the precision and outcomes of coronary artery bypass surgery, which is performed to restore blood flow to the heart muscles when the coronary arteries may be blocked or narrowed due to coronary artery disease. However, robotic CABG utilizes advanced robotic systems to assist surgeons in performing these bypass grafts with greater precision and control.
Here’s how robotic CABG typically works:
Robotic System Setup: The surgical team sets up a robotic surgical system, which includes a console where the surgeon sits, robotic arms equipped with surgical instruments, and a high-definition camera that provides a detailed view of the surgical site.
Patient Preparation: The patient undergoes general anesthesia to ensure they are unconscious and pain-free during the procedure. Monitoring devices are used to track vital signs throughout the surgery.
Small Incisions: Instead of a large incision in the chest as in traditional CABG, robotic CABG involves making several small incisions (keyhole incisions) in the chest. These smaller incisions reduce trauma to the surrounding tissues.
Robotic Assistance:The surgeon controls the robotic arms from the console, maneuvering the surgical instruments with precision. The robotic system provides magnified, high-definition 3D images of the surgical site, allowing for better visualization.
Graft Placement: Using the robotic arms and instruments, the surgeon harvests blood vessels (often from the patient’s leg or chest) to create bypass grafts. These grafts are then attached to the blocked or narrowed coronary arteries to bypass the obstruction and restore blood flow to the heart muscles.
Closure and Recovery: After completing the grafting procedure, the surgeon closes the incisions using sutures or surgical staples. The patient is then moved to a recovery area where they are monitored closely as they wake up from anesthesia. Here are key points about robotic CABG:
Robotic Systems: Robotic CABG uses sophisticated robotic surgical systems that consist of a console where the surgeon sits, robotic arms equipped with surgical instruments, and a high-definition camera for enhanced visualization.
Reduced Blood Loss: Due to the minimally invasive nature and precise control offered by robotic systems, there is often less blood loss during robotic CABG procedures compared to traditional surgery.
Quicker Recovery: Patients undergoing robotic CABG typically experience faster recovery times and can return to normal activities sooner than those undergoing traditional CABG. This is partly due to the smaller incisions and reduced trauma to surrounding tissues.
Minimally Invasive: One of the primary advantages of robotic CABG is that it can be performed through smaller incisions compared to traditional open-heart surgery. This leads to reduced trauma, less pain, shorter hospital stays, and quicker recovery times for patients.
Enhanced Precision: The robotic system provides the surgeon with magnified, high-definition 3D images of the surgical site, allowing for precise movements and accurate graft placement. This precision can lead to improved outcomes and reduced risks during surgery.
Reduced Risk of Complications: The minimally invasive nature of robotic CABG may lead to lower risks of infections, bleeding, and other complications commonly associated with open-heart surgery.
Overall, robotic CABG represents a significant advancement in cardiac surgery, offering patients a less invasive option with potential benefits in terms of recovery, outcomes, and overall surgical experience. However, the decision to undergo robotic CABG should be made in consultation with a qualified cardiac surgeon based on individual medical needs and considerations. Factors such as the patient’s overall health, the complexity of the coronary artery disease, and the surgeon’s experience with robotic surgery will influence candidacy and treatment options.