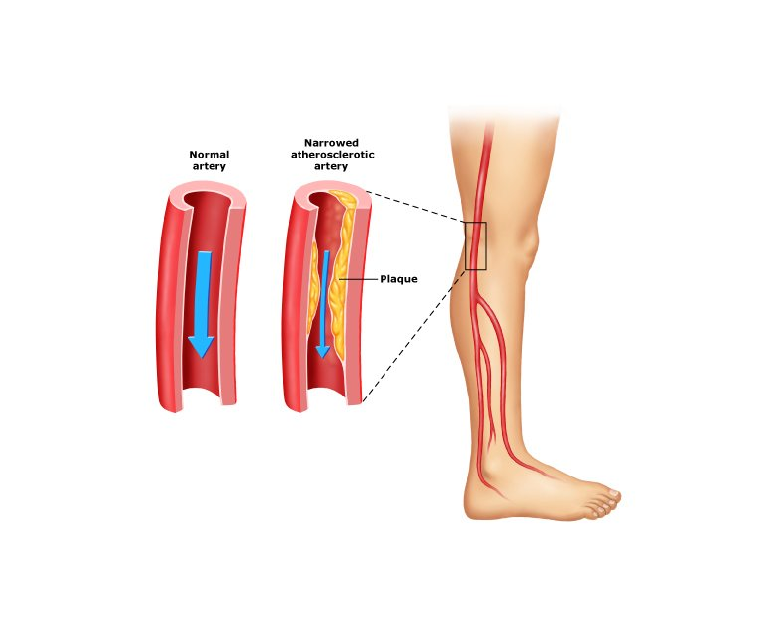
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a circulatory condition that affects the peripheral arteries, which are the blood vessels that carry blood from the heart to the arms, legs, and other parts of the body. PAD occurs when these arteries become narrow or blocked, reducing blood flow to the affected body parts. The most common symptoms of PAD include pain, numbness, and cramping in the legs or feet, especially during physical activity.
How is PAD caused?
PAD is caused by atherosclerosis, a condition in which fatty deposits, or plaques, build up inside the arteries, narrowing the blood vessels and restricting blood flow. Atherosclerosis can affect any artery in the body, but it is most commonly found in the peripheral arteries of the legs and feet. Other risk factors for PAD include smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, obesity, and a family history of the disease.
PAD can be a serious condition, and if left untreated, it can lead to complications such as foot ulcers, gangrene, and amputation. However, there are a number of treatments available for PAD, and early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent these complications and improve quality of life.
Treatment
The first step in treating PAD is to make lifestyle changes that can help improve blood flow and reduce the risk of further narrowing of the arteries. These may include quitting smoking, losing weight, exercising regularly, and following a healthy diet.
Medications may also be prescribed to help manage symptoms and reduce the risk of complications. Some of the most commonly used medications for PAD include antiplatelet agents, such as aspirin or clopidogrel, which can help prevent blood clots from forming in the narrowed arteries, and statins, which can help lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of further plaque build-up.
In more severe cases of PAD, surgical or minimally invasive procedures may be necessary to restore blood flow to the affected areas. These procedures may include angioplasty, in which a small balloon is inserted into the narrowed artery and inflated to widen the artery and improve blood flow, or stenting, in which a small metal mesh tube is placed in the artery to hold it open.
In some cases, bypass surgery may be necessary, in which a healthy blood vessel is taken from another part of the body and used to bypass the blocked artery, allowing blood to flow freely to the affected area.
If left untreated, PAD can lead to serious complications, including foot ulcers, gangrene, and amputation. However, with proper diagnosis and treatment, the prognosis for PAD is generally good. By making lifestyle changes, taking medication as prescribed, and undergoing any necessary procedures, most people with PAD can improve their symptoms, reduce their risk of complications, and maintain their mobility and quality of life.
Conclusion
PAD is a common circulatory condition that can cause pain, numbness, and cramping in the legs and feet, especially during physical activity. It is caused by atherosclerosis, and risk factors include smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, obesity, and a family history of the disease. Treatment for PAD may include lifestyle changes, medications, or surgical procedures, depending on the severity of the condition. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent complications and improve quality of life for people with PAD.