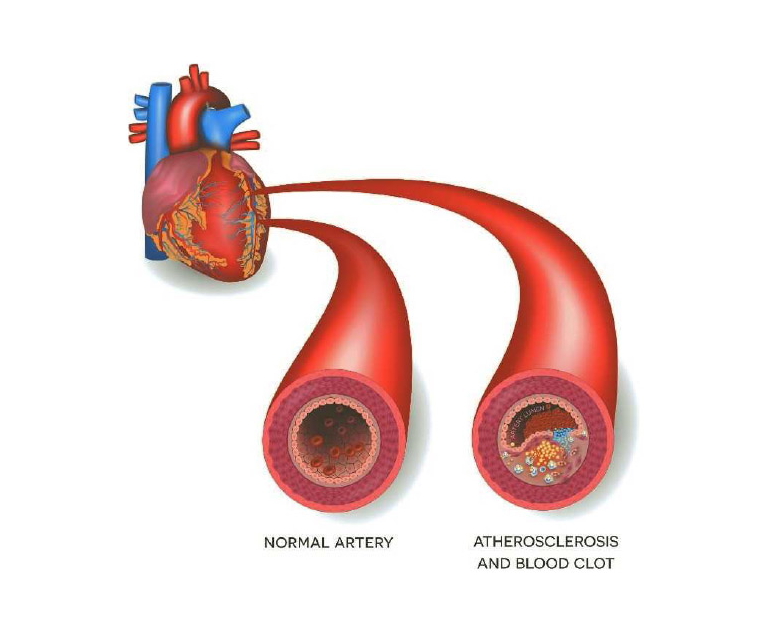
Atherosclerosis is a progressive condition in which the arteries become narrowed and hardened due to the buildup of plaque on their inner walls. Here is a more detailed explanation of the key aspects of atherosclerosis:
Plaque Formation: The process begins with damage to the inner lining (endothelium) of an artery. High blood pressure, smoking, high levels of cholesterol and triglycerides, and inflammation are some of the factors that can cause this damage. The endothelium’s damage causes the accumulation of substances like low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and white blood cells at the site of injury.
Inflammatory Response: The immune system responds to the accumulation of these substances by initiating an inflammatory response. This causes the formation of fatty streaks, which are the early stages of plaque development.
Plaque Growth: Over time, the fatty streaks can progress into more complex plaques. These plaques consist of a core of cholesterol, calcium deposits, and other substances covered by a fibrous cap. As the plaque grows, it can protrude into the arterial lumen, narrowing the blood vessel.
Arterial Narrowing and Hardening: The accumulation of plaque leads to the narrowing of the arteries, reducing blood flow to organs and tissues. The plaque can also harden and calcify, making the arteries less elastic.
Reduced Blood Flow and Ischemia: As the arteries become progressively narrowed, the blood flow to vital organs and tissues decreases. This reduced blood flow can result in ischemia, which is an insufficient supply of oxygen and nutrients to the affected tissues.
Clinical Consequences: The consequences of atherosclerosis depend on the location of the affected arteries. If it occurs in the coronary arteries, it can lead to coronary artery disease and may result in angina (chest pain) or a heart attack. Atherosclerosis in the arteries supplying the brain can lead to cerebrovascular disease and increase the risk of stroke. In the peripheral arteries, it can cause peripheral artery disease, affecting the limbs and causing symptoms such as pain and difficulty walking.
Risk Factors and Prevention: Risk factors for atherosclerosis include high blood pressure, smoking, high cholesterol levels, diabetes, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle. Prevention and management strategies involve adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, maintaining a healthy weight, managing blood pressure and cholesterol levels, and avoiding smoking.
Treatment approaches may include lifestyle modifications, medications to control risk factors, and, in some cases, invasive procedures such as angioplasty or bypass surgery to address severely blocked arteries. Early detection and management are crucial in preventing the progression of atherosclerosis and its associated complications.