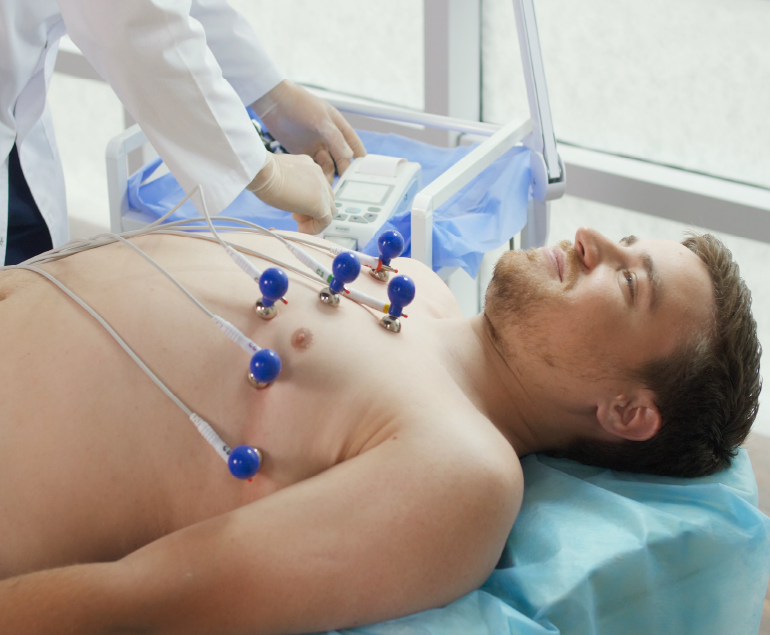
Dobutamine Stress Echocardiogram, also known as DSE, is a non-invasive diagnostic test used to evaluate the function and blood flow of the heart. This test is commonly performed to detect and assess the severity of coronary artery disease or other conditions that may affect the heart’s ability to pump blood efficiently.
During a DSE, the patient is given a medication called dobutamine, which is a synthetic version of the hormone dopamine. This medication stimulates the heart, causing it to beat faster and harder, similar to what happens during exercise. As a result, the heart’s blood flow and function can be evaluated under conditions of increased stress.
An echocardiogram machine is used to generate images of the heart, while the dobutamine is administered through an intravenous (IV) line. The dose of dobutamine is gradually increased over several stages, while the heart is monitored using electrocardiogram (ECG) and echocardiogram (ultrasound) equipment.
The test is divided into several stages, and during each stage, the patient’s heart rate and blood pressure are monitored to evaluate the heart’s response to the medication. The stages are typically categorized based on the level of stress placed on the heart, ranging from rest to peak exertion. The test usually takes about 30 to 60 minutes to complete, depending on the patient’s response to the medication.
One of the main advantages of a DSE over other types of stress tests is that it does not require physical exertion, making it a safer option for patients who may not be able to exercise due to other medical conditions. Additionally, a DSE provides a more comprehensive evaluation of the heart’s function than other non-invasive tests, such as a resting echocardiogram or stress electrocardiogram.
The DSE test is commonly used to diagnose and assess the severity of coronary artery disease (CAD), which occurs when the arteries that supply blood to the heart become narrowed or blocked. CAD can lead to chest pain, heart attack, or other serious complications if left untreated. During a DSE, areas of the heart that are not receiving enough blood flow due to narrowed or blocked arteries can be identified, allowing doctors to determine the best treatment options.
In addition to CAD, a DSE can also be used to diagnose and evaluate other heart conditions, such as heart valve disease, cardiomyopathy, or pulmonary hypertension. By evaluating the heart’s function under conditions of increased stress, doctors can better understand how these conditions are affecting the heart’s ability to pump blood efficiently.
In conclusion, a Dobutamine Stress Echocardiogram is a safe and effective non-invasive test used to evaluate the function and blood flow of the heart. It is a valuable tool in the diagnosis and management of various heart conditions, including coronary artery disease and heart valve disease. By providing a comprehensive evaluation of the heart’s function under conditions of increased stress, doctors can better understand how these conditions are affecting the heart and develop an appropriate treatment plan.