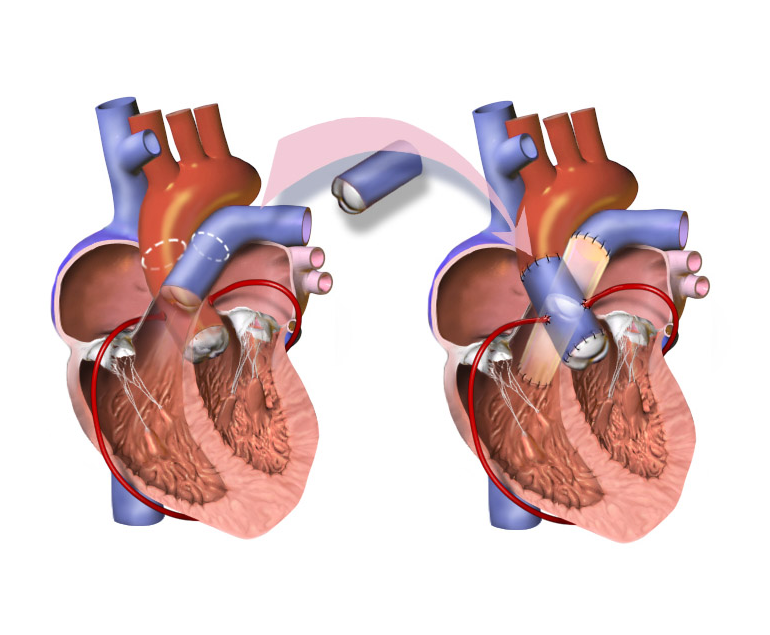
The Ross procedure is a surgical procedure used to treat aortic valve disease, which is a condition in which the valve that controls blood flow from the heart to the aorta becomes narrowed or leaks. This procedure involves replacing the damaged aortic valve with the patient’s own pulmonary valve, and then replacing the pulmonary valve with a donated or artificial valve.
The Ross procedure is named after its creator, Donald Ross, a Scottish cardiac surgeon who developed the technique in the 1960s. Since then, the procedure has become a popular option for treating aortic valve disease in certain patients.
Advantages of Ross Procedure
The Ross procedure is typically recommended for younger patients who have aortic valve disease, as it has several advantages over other types of valve replacement surgery. One of the main advantages is that it avoids the need for lifelong anticoagulation therapy, which is required for patients who receive a mechanical valve replacement. Anticoagulation therapy is a type of medication that helps prevent blood clots, but it can also increase the risk of bleeding and other complications.
Another advantage of the Ross procedure is that it provides a better quality of life for patients. The pulmonary valve is better suited to the low-pressure environment of the aortic position than artificial valves, which can often lead to complications such as valve dysfunction or blood clots.
Procedure
The Ross procedure is performed under general anaesthesia and typically takes many hours to complete. During the procedure, the surgeon will make an incision in the chest and access the heart. The patient’s pulmonary valve will then be removed and used to replace the damaged aortic valve. A new pulmonary valve, either from a donated cadaver or an artificial valve, will then be used to replace the removed pulmonary valve.
After the procedure, patients may need to spend several days in the hospital recovering. They may experience some discomfort or pain, and will need to take medication to manage pain and prevent infection. Patients will also need to gradually increase their physical activity and follow a prescribed rehabilitation program to help them recover.
Suitability
While the Ross procedure has many benefits, it is not suitable for all patients with aortic valve disease. Patients who have other heart conditions, such as coronary artery disease or an enlarged heart, may not be good candidates for the procedure. Additionally, patients who have already had a previous valve replacement or who have other medical conditions that could complicate surgery may not be good candidates for the procedure.
Conclusion
Ross procedure is a surgical procedure used to treat aortic valve disease in certain patients. It involves replacing the damaged aortic valve with the patient’s own pulmonary valve, and then replacing the pulmonary valve with a donated or artificial valve. If you are considering the Ross procedure, it is important to discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor to determine if it is the right option for you.