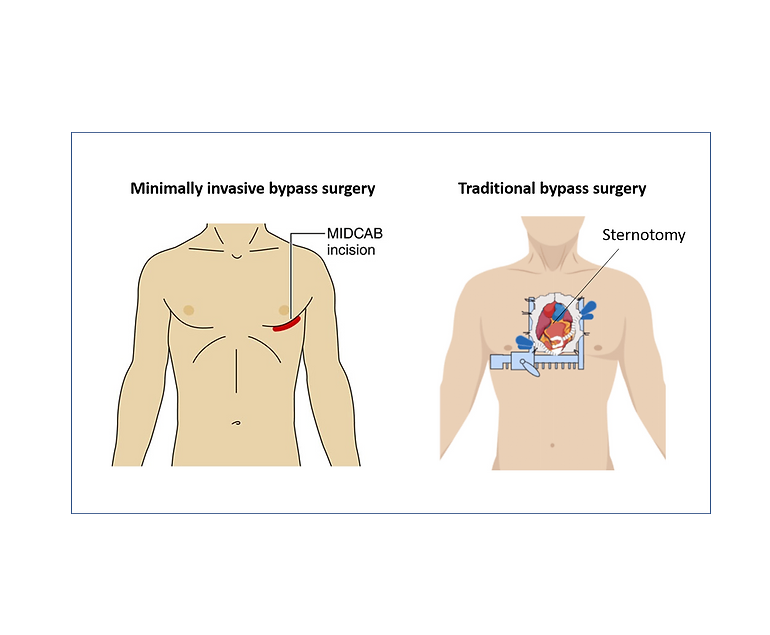
Minimally Invasive Direct Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (MIDCAB) is a less invasive surgical procedure for treating coronary artery disease (CAD). Unlike traditional coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), which requires a median sternotomy and the use of a heart-lung machine, MIDCAB is performed through a small incision on the left side of the chest, offering several advantages.
Procedure Highlights
- Small Incision: MIDCAB involves a small incision between the ribs, eliminating the need for a sternotomy. This results in less chest trauma and reduced postoperative pain.
- On-Beating Heart: Unlike traditional CABG, which temporarily stops the heart with a heart-lung machine, MIDCAB is performed on a beating heart. This reduces the risk of complications associated with bypassing the heart’s normal function.
- Shorter Recovery: Patients undergoing MIDCAB experience a shorter hospital stay and a faster return to their regular activities, making it an appealing option for those seeking quicker recovery.
- Reduced Scarring: The small incision in MIDCAB results in less visible scarring, providing cosmetic benefits for some patients.
Patient Eligibility
MIDCAB is suitable for patients with single or double-vessel disease, meaning they have blockages in one or two coronary arteries. It is not appropriate for complex multi-vessel disease requiring multiple grafts. Favorable patient anatomy and good overall health are essential for candidacy.
Procedure Steps
- Incision: A small incision is made between the ribs on the left side of the chest to access the target coronary artery.
- Graft Placement: A healthy blood vessel, often the internal mammary artery or radial artery, is harvested and prepared for grafting. It is then attached to the blocked coronary artery, creating a new pathway for blood flow.
- Heart Monitoring: Specialized equipment is used to monitor the heart throughout the procedure to ensure it continues to beat.
- Closure: After successfully placing the graft, the incision is closed, and the chest is sutured. No sternotomy is required.
Benefits and Considerations
Advantages:
- Less Invasive: MIDCAB results in reduced chest trauma, postoperative pain, and discomfort.
- Quicker Recovery: Patients have a faster recovery and shorter hospital stay.
- Cosmetic Appeal: The small incision leads to less visible scarring.
Considerations:
- Limited Applicability: MIDCAB is suitable only for patients with single or double-vessel disease.
- Long-Term Efficacy: Long-term outcomes compared to traditional CABG are still under investigation.
- Operator Skill: MIDCAB requires a highly skilled and experienced surgeon.
- Patient Selection: Careful patient evaluation is crucial to ensure the best outcomes.
Summary
Minimally Invasive Direct Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (MIDCAB) is an attractive option for many patients with CAD due to its less invasive nature, faster recovery, and improved cosmetic results. However, patient suitability and careful evaluation by doctors are key factors in determining the most appropriate treatment approach.