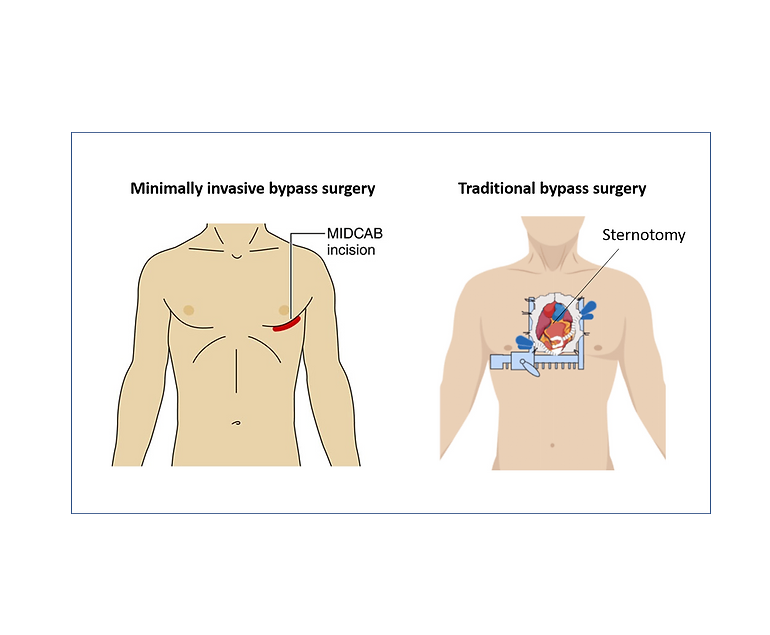
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) surgery is often a part of comprehensive treatment for coronary artery disease. After undergoing CABG, individuals are typically advised to make certain lifestyle changes to promote heart health and reduce the risk of further cardiovascular issues.
Lifestyle changes after Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) are crucial for promoting cardiovascular health, reducing the risk of future heart issues, and enhancing overall well-being. Here’s a closer look at how lifestyle changes are typically implemented after CABG:
- Dietary Modifications:
• Heart-Healthy Diet: Patients are often advised to adopt a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and sources of omega-3 fatty acids. Limiting saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium is emphasized. - Regular Exercise:
• Gradual Progression: Patients are encouraged to engage in regular aerobic exercises like walking, cycling, or swimming. Exercise is typically introduced gradually, considering the individual’s physical condition and recovery progress.
• Customized Exercise Plans: Exercise programs are often tailored to individual needs, and healthcare professionals provide guidance on the type, duration, and intensity of exercises. - Smoking Cessation:
• Quit Smoking: Quitting smoking is a top priority. Healthcare providers offer support and resources to help individuals overcome nicotine addiction. - Medication Adherence:
• Prescription Medications: Patients are prescribed medications to manage conditions such as hypertension, high cholesterol, and diabetes. Adherence to medication regimens is critical for preventing further cardiovascular complications. - Weight Management:
• Healthy Weight Goals: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight is emphasized, often through a combination of dietary adjustments and regular physical activity. - Stress Management:
• Relaxation Techniques: Stress management techniques, such as mindfulness, meditation, and deep breathing exercises, are recommended to help individuals cope with stress and promote emotional well-being. - Regular Follow-up Appointments:
• Health Monitoring: Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are essential for monitoring overall health, adjusting medications, and addressing any emerging health concerns. - Limiting Alcohol Intake:
• Moderation: If alcohol is consumed, it should be in moderation. Healthcare professionals provide guidance on safe levels of alcohol intake based on individual health conditions. - Educational Programs and Support Groups:
• Information and Support: Participation in educational programs and support groups can provide valuable information, encouragement, and a sense of community. This helps individuals stay informed and motivated to make positive lifestyle changes. - Sleep Hygiene:
• Quality Sleep: Ensuring adequate and quality sleep is important for recovery and overall health. Addressing sleep-related issues, such as sleep apnea, may be part of the plan. - Hydration:
• Adequate Fluid Intake: Staying well-hydrated is important for general health. Limiting the intake of sugary and caffeinated beverages may be recommended.
Patients are encouraged to work collaboratively with their healthcare team, which may include cardiologists, nutritionists, physical therapists, and mental health professionals. The implementation of these lifestyle changes is typically gradual, and the plan is often tailored to the individual’s unique circumstances, health status, and preferences. Consistent follow-up and ongoing support contribute to the success of these lifestyle modifications after CABG.
Lifestyle changes after Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) are crucial for promoting cardiovascular health, reducing the risk of future heart issues, and enhancing overall well-being. Here’s a closer look at how lifestyle changes are typically implemented after CABG: