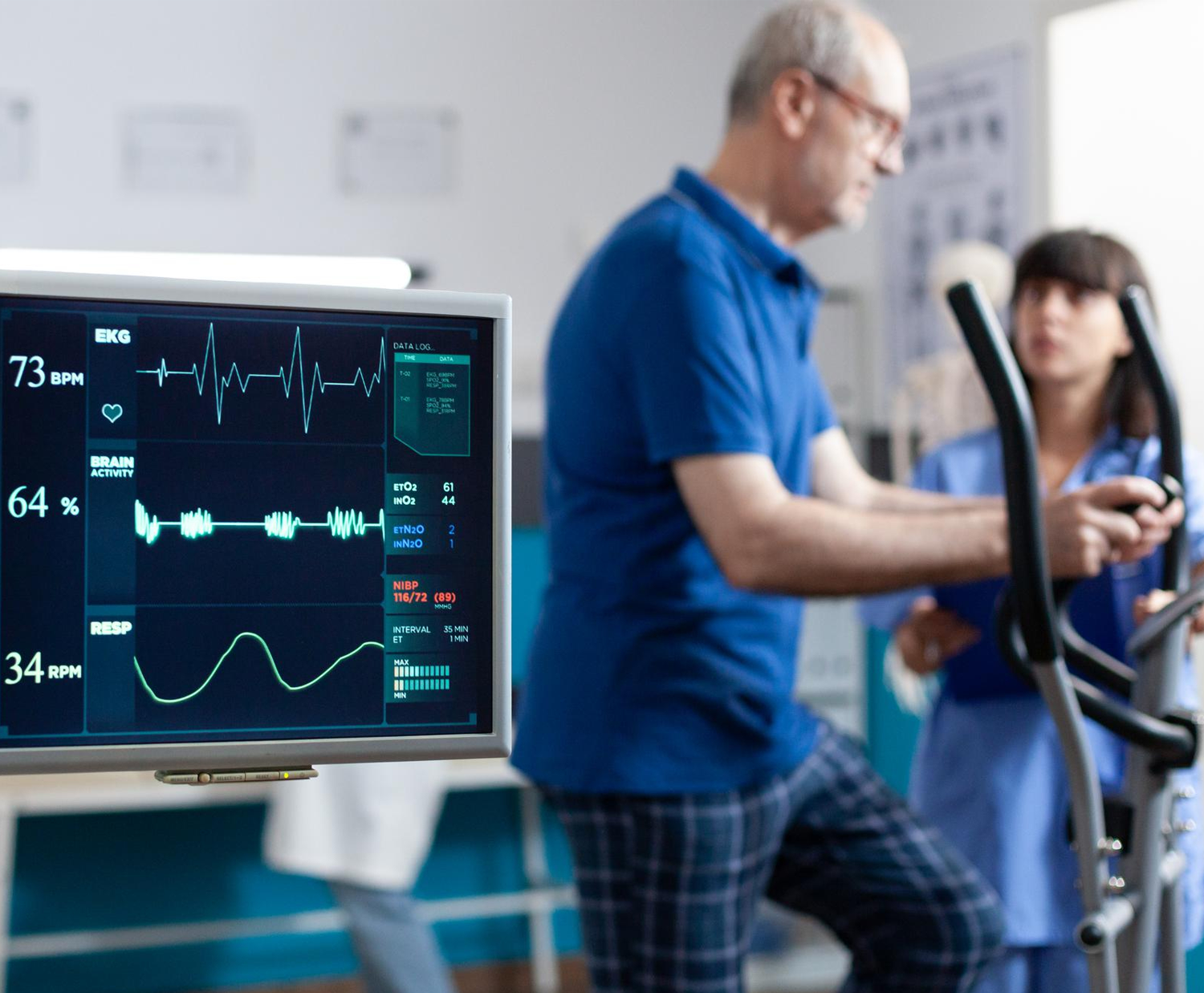
Cardiac rehabilitation (CR) is a structured and medically supervised program designed to help individuals recover from various heart-related conditions and improve their cardiovascular health. The primary focus of cardiac rehabilitation is to enhance the overall well-being of individuals who have experienced a heart attack, undergone heart surgery, or are living with conditions such as heart failure, coronary artery disease, or angina.
The core components of cardiac rehabilitation typically include:
- Medical Assessment: Before starting a cardiac rehabilitation program, individuals undergo a thorough medical assessment to evaluate their current health status, identify risk factors, and create a personalized plan for rehabilitation.
- Exercise Training: Regular, supervised exercise sessions are a fundamental aspect of cardiac rehabilitation. These sessions aim to improve cardiovascular fitness, endurance, and strength. Exercise programs are tailored to the individual’s health status, ensuring safety and gradual progression.
- Education: Patients receive education on heart health, risk factors, lifestyle modifications, and self-management strategies. This includes information on nutrition, medication management, and stress reduction to empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health.
- Behavioral Counseling: Psychosocial support is provided to address the emotional and psychological aspects of living with heart disease. Counseling may cover stress management, coping strategies, and mental health support.
- Nutritional Counseling: Dietary guidance is offered to help individuals adopt heart-healthy eating habits. This may involve managing weight, reducing sodium intake, and making nutritious food choices to control factors like high blood pressure and cholesterol.
- Risk Factor Modification: Cardiac rehabilitation emphasizes lifestyle changes to address and modify risk factors associated with heart disease. This includes smoking cessation, weight management, and strategies to control conditions like diabetes.
- Medication Management: Education and support are provided to help individuals understand and manage their medications effectively. This includes information on medication adherence and potential side effects.
- Monitoring and Follow-up: Regular monitoring of progress and follow-up assessments are conducted to track improvements and adjust the rehabilitation plan as needed. Follow-up care is essential to maintain and reinforce positive lifestyle changes.
According to Dr. Ramji Mehrotra, Cardiac rehabilitation is typically conducted in a specialized outpatient setting, and programs may vary in duration (typically lasting several weeks to a few months). The involvement of a multidisciplinary team, including physicians, nurses, exercise physiologists, dietitians, and psychologists, ensures a comprehensive approach to care.
Participation in cardiac rehabilitation has been associated with numerous benefits, including improved exercise capacity, reduced symptoms, lower rates of hospitalization, and enhanced quality of life for individuals with cardiovascular diseases. It plays a crucial role in the continuum of care for those recovering from heart events or managing chronic heart conditions.