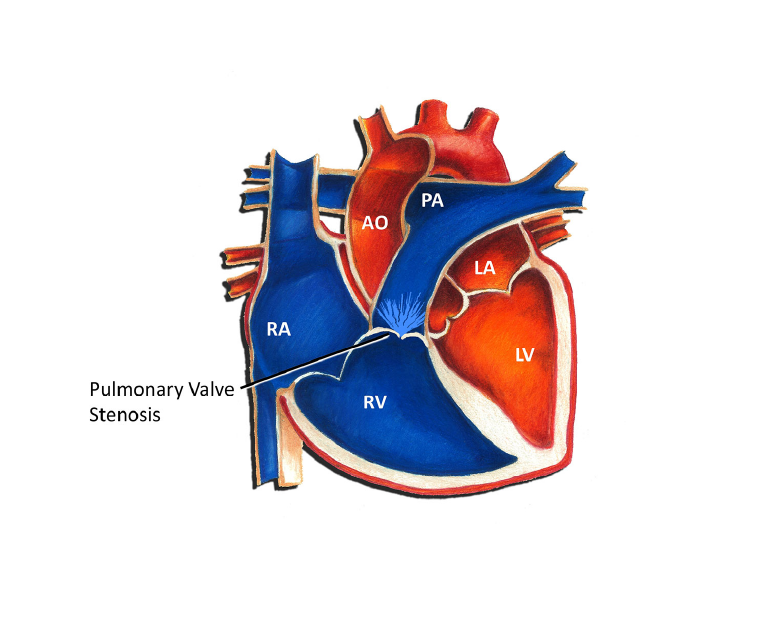
Pulmonary valve stenosis is a medical condition in which the pulmonary valve, which regulates blood flow from the right ventricle of the heart to the lungs, becomes narrowed or obstructed. This can lead to difficulty breathing and reduced oxygen levels in the blood, causing a range of symptoms and potentially serious health complications if left untreated.
Causes of Pulmonary Valve Stenosis
There are several potential causes of pulmonary valve stenosis. One common cause is congenital heart defects, which are present at birth and may be inherited or caused by environmental factors during pregnancy. Rheumatic fever, a condition that can develop as a complication of strep throat, can also lead to pulmonary valve stenosis. In rare cases, the valve may become narrowed or obstructed due to scarring or inflammation. In some cases, the cause of the stenosis is unknown.
Symptoms
Symptoms of pulmonary valve stenosis can vary depending on the severity of the condition. In mild cases, individuals may not experience any symptoms or may only have mild shortness of breath during physical activity. More severe cases may cause significant difficulty breathing, chest pain, fatigue, and fainting. In severe cases, the condition can also cause heart palpitations, swelling in the legs and ankles, and a bluish tint to the skin due to low oxygen levels.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis of pulmonary valve stenosis typically begins with a physical exam and a review of the individual’s medical history. The doctor may also order several tests to confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity of the condition. These tests may include an echocardiogram, a chest X-ray, and an electrocardiogram.
There are several treatment options available for pulmonary valve stenosis, depending on the severity of the condition and the individual’s overall health. In mild cases, treatment may include medications to manage symptoms and reduce the risk of complications. These may include diuretics to reduce fluid build-up in the body and beta blockers to reduce the heart’s workload.
For more severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or replace the valve. Repair surgery involves making changes to the existing valve to improve its function, while valve replacement surgery involves replacing the faulty valve with a new one. There are several different types of valves that can be used in replacement surgery, including mechanical valves, which are made of man-made materials, and biological valves, which are made from animal tissue.
In some cases, a procedure called balloon valvuloplasty may be used to widen the narrowed valve. This procedure involves inserting a balloon catheter into the narrowed valve and inflating the balloon to widen the opening.
It is important for patients with pulmonary valve stenosis to work closely with their doctors to manage their condition and reduce the risk of complications. This may include regular check-ups and monitoring of symptoms, lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking and eating a healthy diet, and taking prescribed medications as directed.
Conclusion
Pulmonary valve stenosis is a serious condition that can have a significant impact on an individual’s quality of life. With proper treatment and management, however, it is possible to live a full and active life. It is important for individuals with the condition to stay in close communication with their doctors and follow their treatment plan to ensure the best possible outcomes.