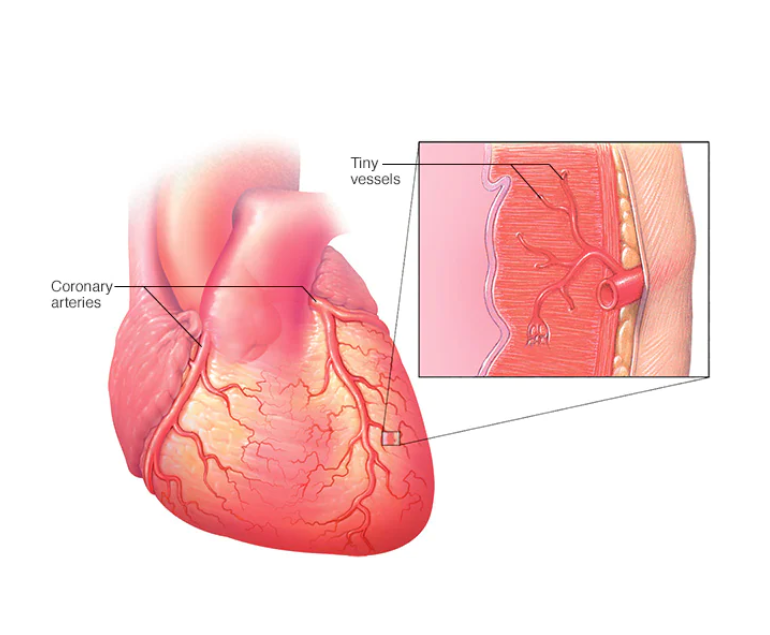
Coronary microvascular disease (CMD) is a condition that affects the small blood vessels in the heart. It is a common cause of chest pain and can also lead to heart failure. While CMD is often overlooked, it is a serious condition that can have significant consequences for people who have it.
How is CMD Caused?
CMD is caused by a blockage or damage to the small blood vessels in the heart, which can reduce blood flow to the heart muscle. This can cause chest pain, shortness of breath, and other symptoms. It can also lead to heart failure, in which the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs.
CMD is often difficult to diagnose because the symptoms can be similar to those of other conditions such as angina or heart attack. In addition, traditional tests such as angiography may not be able to detect the blockages or damage in the small blood vessels. As a result, CMD may be misdiagnosed or go undiagnosed for some time.
Risk Factors
Risk factors for CMD include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, and smoking. It is also more common in women and people with a family history of heart disease. These risk factors can damage the small blood vessels in the heart and lead to CMD.
Treatment of CMD
The good news is that CMD is a treatable condition. The first step in treatment is to manage any underlying risk factors such as high blood pressure or high cholesterol. This may involve lifestyle changes such as eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and quitting smoking. In some cases, medications may be necessary to lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels and improve blood flow to the heart.
In addition to managing risk factors, it is important to address any symptoms of CMD. This may involve the use of medications to manage chest pain and improve blood flow to the heart. In some cases, procedures such as angioplasty or stenting may be necessary to open blocked blood vessels.
It is important to regularly consult with the specialist who can develop a treatment plan to manage CMD. This may include regular check-ups, blood pressure monitoring, and medication management. By taking steps to manage CMD, patients can reduce their risk of heart failure and other serious complications.
Conclusion
CMD is a serious condition that affects the small blood vessels in the heart. It can cause chest pain and lead to heart failure if left untreated. Risk factors for CMD include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, and smoking. Treatment may involve lifestyle changes and medications, and in some cases, procedures to open blocked blood vessels.