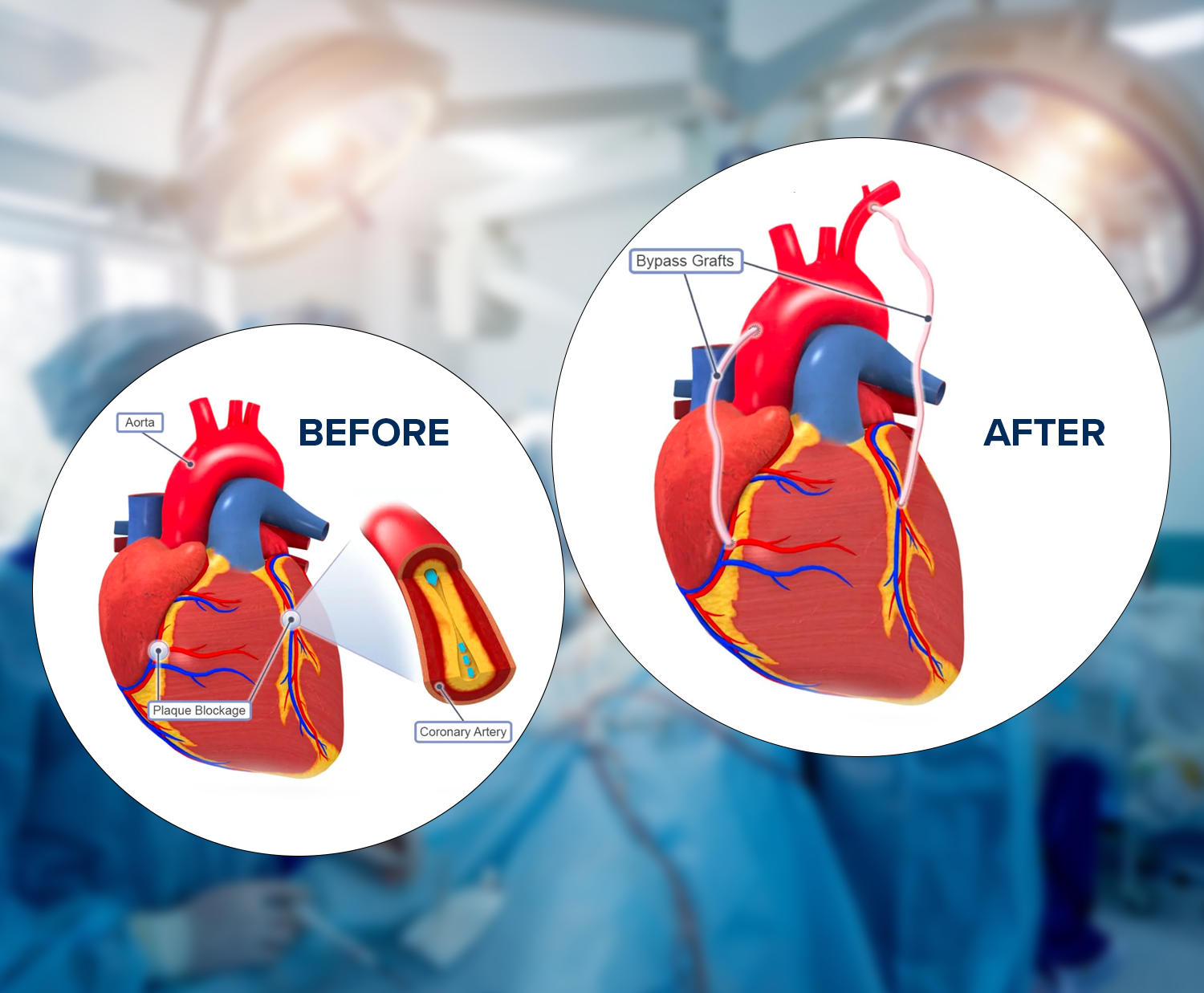
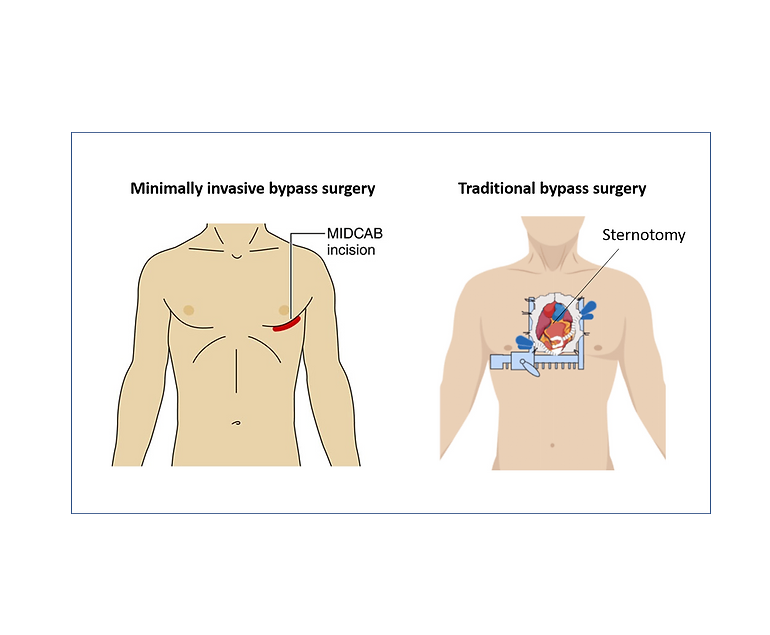
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) is a surgical procedure commonly performed to treat coronary artery disease (CAD), a condition in which the blood vessels supplying the heart muscle (coronary arteries) become narrowed or blocked. CABG is also known as heart bypass surgery. Here is an overview of the CABG procedure:
1. Preoperative Evaluation:
Medical History and Physical Examination: A physical examination is performed after assessing the patient’s medical history and overall health.
Diagnostic Tests: These may include an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), an echocardiogram, coronary angiography, and other imaging tests to evaluate the extent and location of coronary artery disease.
2. Anesthesia:
Pre-anesthetic Assessment: The anesthesiologist evaluates the patient’s overall health and determines the appropriate anesthesia plan.
General Anesthesia: During surgery, the patient is put under general anesthesia, which makes them unconscious and pain-free.
3. Harvesting of Grafts:
Graft Selection: Healthy blood vessels, often taken from the patient’s own body (autografts) or occasionally from a donor (allografts), are chosen for bypass grafts. Commonly used vessels include the internal mammary artery, radial artery, and saphenous vein.
4. Surgical Access:
Sternotomy or Thoracotomy: A sternotomy (cutting through the breastbone) is the most common approach, but in some cases, a thoracotomy (a small incision between the ribs) may be used.
5. Cardiopulmonary Bypass (if needed):
Connecting to a Heart-Lung Machine: The heart may be temporarily stopped, and blood is rerouted through a heart-lung machine, providing oxygen and circulation for the body while allowing the surgeon to work on a still heart.
6. Graft Placement:
Bypassing Blockages: The surgeon attaches one end of the graft to the aorta and the other end to a coronary artery beyond the blockage, creating a new pathway for blood flow.
7. Weaning off Bypass and Closing:
Restoration of Blood Flow: If a heart-lung machine is used, the patient is gradually weaned off it, and the heart resumes pumping.
Restoration of Blood Flow: If a heart-lung machine is used, the patient is gradually weaned off it, and the heart resumes pumping.
Closure: The chest has been closed, and the incision has been sutured.
8. Postoperative Care:
Monitoring: Initially, the patient is monitored closely in the intensive care unit (ICU) before being moved to a regular room.
Recovery: Rehabilitation and recovery involve medications, lifestyle changes, and follow-up care to ensure a smooth recovery.
9. Potential Risks and Complications:
Infection, bleeding, or blood clots: As with any surgery, there are potential risks, and complications can arise. The medical team closely monitors the patient to address any issues promptly.
According to Dr. Ramji Mehrota – Best Heart Specialist Doctor in India, It’s important to note that the specifics of the procedure can vary based on individual patient characteristics and the surgeon’s preference. CABG is considered a major surgery, and the decision to undergo the procedure is made after a thorough assessment of the patient’s condition and the benefits of surgery. For personalized information, it’s best to consult healthcare professionals.
It’s important to note that the specifics of the procedure can vary based on individual patient characteristics and the surgeon’s preference. CABG is considered a major surgery, and the decision to undergo the procedure is made after a thorough assessment of the patient’s condition and the benefits of surgery. For personalized information, it’s best to consult healthcare professionals.