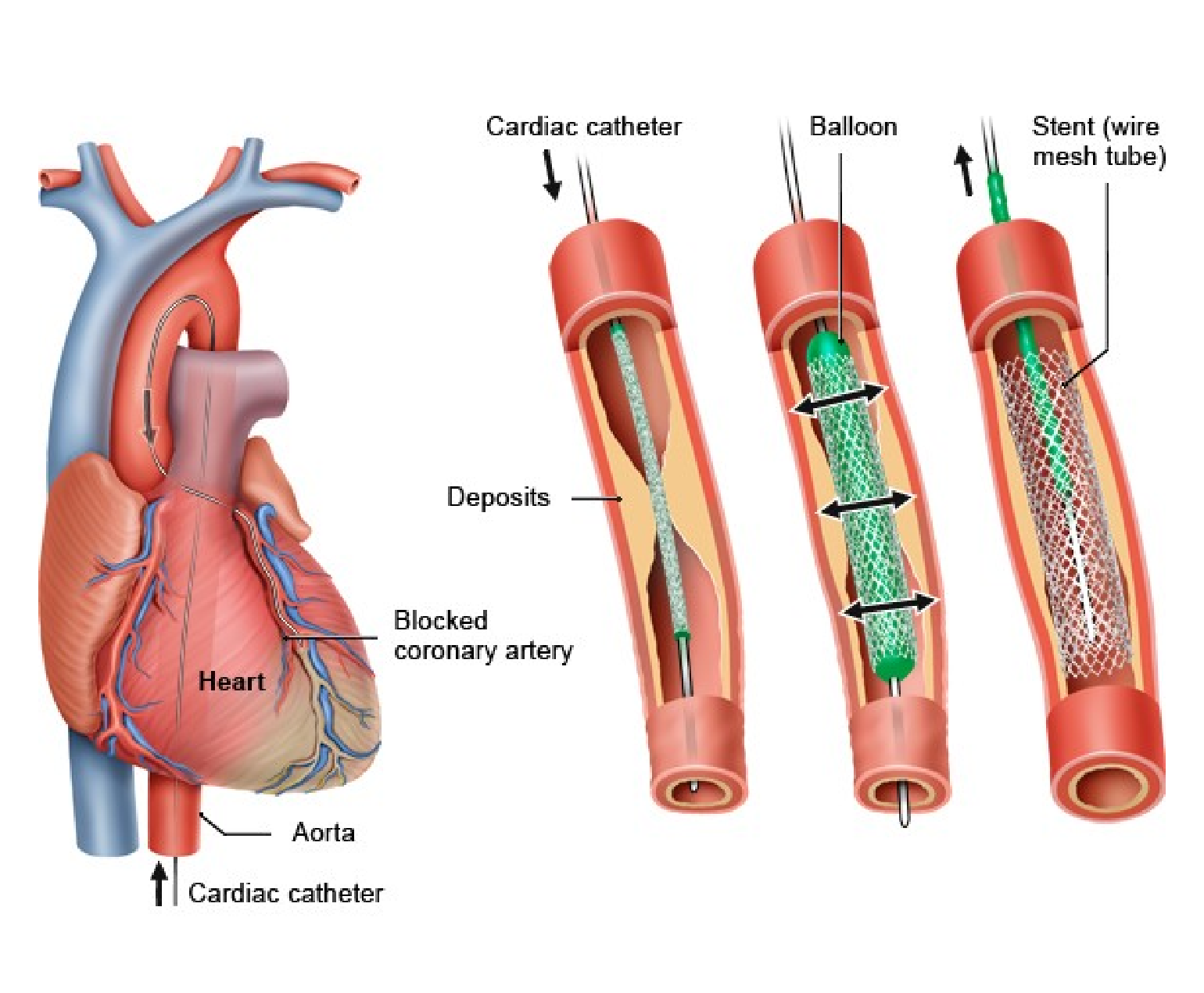
Cardiac catheterization, also known as coronary angiography, is a medical procedure that allows doctors to examine the heart and blood vessels to identify any problems. It is a minimally invasive procedure that involves inserting a thin, flexible tube called a catheter into a blood vessel, typically in the groin or arm, and guiding it through the blood vessels to the heart.
The catheterization procedure is performed in a cardiac catheterization laboratory (also known as a cath lab) by a cardiologist. The procedure is typically done under local anaesthesia, which numbs the area where the catheter will be inserted.
Procedure
During the procedure, the cardiologist will make a small incision in the skin and insert a hollow sheath into the blood vessel. The catheter is then inserted through the sheath and guided to the heart using x-ray guidance. Once the catheter is in place, the cardiologist can inject a contrast dye into the bloodstream, which makes the heart and blood vessels visible on x-ray.
The contrast dye allows the cardiologist to examine the heart and blood vessels for any abnormalities or blockages that may be present. If a blockage is found, the cardiologist can perform a procedure called angioplasty to open the blocked artery and restore blood flow to the heart.
Diagnostic Tool
Cardiac catheterization is a valuable diagnostic tool that can provide important information about the heart and blood vessels. It is typically used to diagnose and evaluate a range of heart conditions, including coronary artery disease, heart valve problems, congenital heart defects, and heart failure.
In addition to providing diagnostic information, cardiac catheterization can also be used to treat certain heart conditions. For example, angioplasty can be used to open blocked arteries and restore blood flow to the heart. Other procedures, such as stent placement and balloon valvuloplasty, can also be performed during cardiac catheterization.
Risks
While cardiac catheterization is generally considered a safe procedure, there are some risks associated with it. These include bleeding, infection, damage to the blood vessels, and allergic reactions to the contrast dye. However, these risks are generally low and can be minimized with proper preparation and monitoring.
Tests before the procedure
Before undergoing cardiac catheterization, patients will typically undergo a series of tests to evaluate their heart health and determine if they are a good candidate for the procedure. These tests may include an electrocardiogram (ECG), echocardiogram, stress test, and blood tests.
Patients should also inform their doctor of any medications they are taking, as some medications may need to be temporarily stopped prior to the procedure. Patients should also avoid eating or drinking anything for several hours before the procedure.
Conclusion
Overall, cardiac catheterization is a valuable tool for diagnosing and treating a range of heart conditions. While there are some risks associated with the procedure, these risks are generally low and can be minimized with proper preparation and monitoring. Patients should talk to their doctor about whether cardiac catheterization is a good option for them and what they can expect during and after the procedure.