Coronary artery disease (CAD) or coronary heart disease is a common type of heart disease that occurs when the arteries become hardened and narrowed. This is caused due to the cholesterol and calcium deposit or plaque in the arteries.
Coronary artery disease begins due to a condition called atherosclerosis which occurs when cholesterol and calcium collects on the inner walls of the arteries. This build-up is known as plaque which can block blood flow due to the narrowing of the arteries. If the plaque bursts it can lead to a blood clot.
Symptoms of CAD
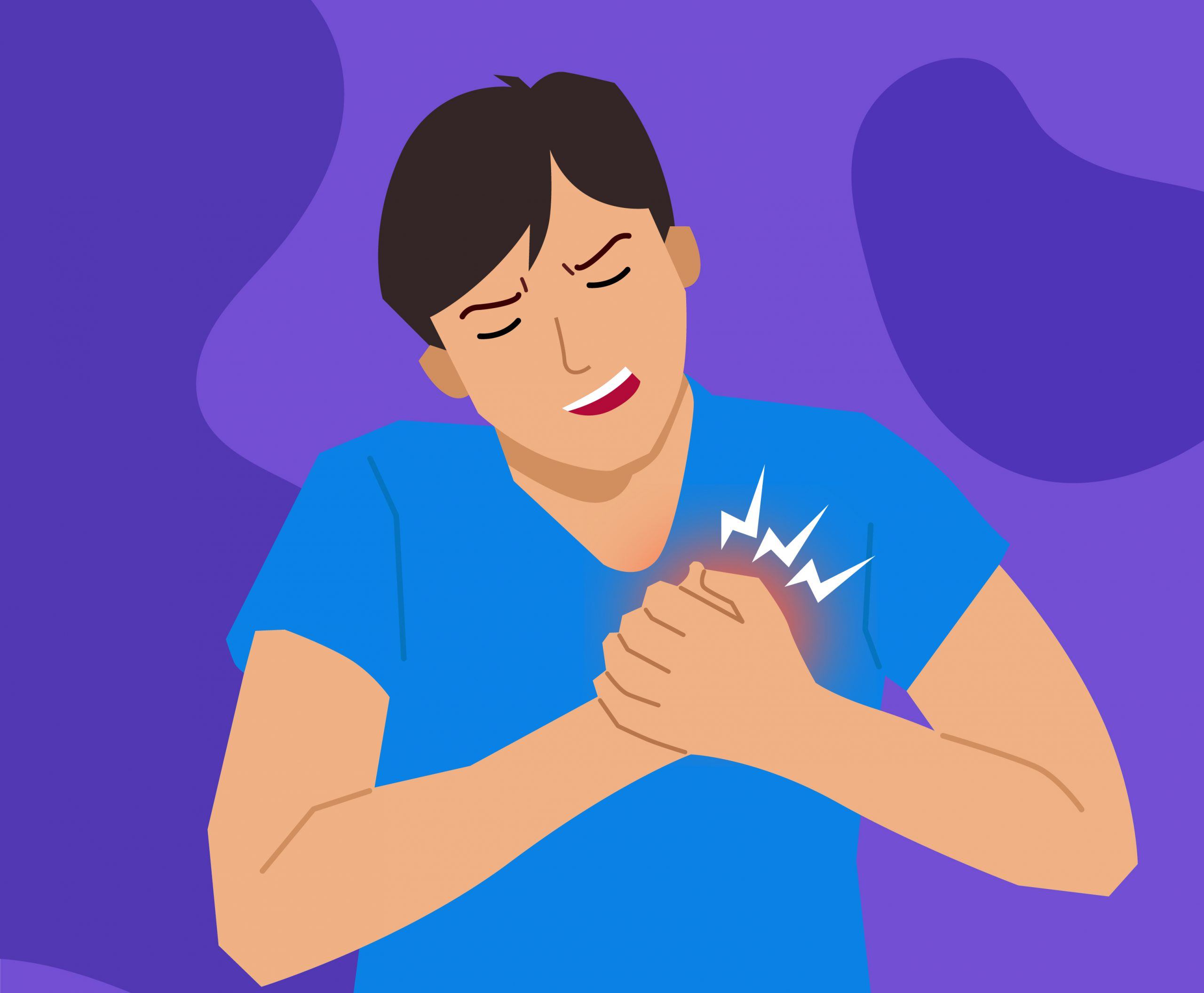
A patient having coronary artery disease can have chest pain, breathlessness, fatigue, nausea and due to the reduced blood flow to the heart. Chest discomfort or angina is accompanied by symptoms like numbness, heaviness, aching, squeezing, etc.
Complete blockage of blood flow can also lead to heart attack.
Risk Factors
In addition to high cholesterol, other causes of damage to coronary arteries include high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking, sedentary lifestyle, etc.
Obesity, stress, unhealthy diet, irregular sleep and alcohol usage are other risk factors for coronary artery disease.
Diagnosis of CAD
The doctor reviews the patient’s symptoms, risk factors and medical history before performing a physical examination. Diagnostic tests include:
- Electrocardiograph test: This test can detect heart attack and heart rhythm issues by recording the heart’s electrical activity.
- Exercise stress test: This is a treadmill test that can help suspect coronary blockages
- Pharmacologic stress test: This test can also help detect coronary blockages through medication given to increase heart rate. This is done in patients who cannot walk on treadmill.
- Coronary calcium scan: This can identify the amount of calcium on the walls of the coronary arteries which can give an indication of atherosclerosis.
- Echocardiogram: This test utilizes sound waves to measure the overall functioning of the heart.
- Blood tests: These tests are done for factors affecting arteries like cholesterol, triglycerides, lipoprotein, glucose, etc.
- Cardiac catheterization: In this test small tubes are inserted into the blood vessels to detect the presence of coronary artery disease and also evaluate the heart function.
Prevention of CAD
According to Dr. Ramji Mehrotra who is one of India’s leading cardiologist, coronary artery disease can be prevented by adopting a healthy lifestyle to improve heart health. These include stopping smoking and limiting alcohol use, consuming a heart-healthy diet, exercising and increasing activity levels, etc.
Blood pressure, diabetes and cholesterol should be controlled. Stress management is also essential to prevent coronary artery disease.