Heart disease, also known as cardiovascular disease, refers to a range of conditions that affect the heart and blood vessels. The heart is a vital organ that pumps blood throughout the body, and its proper functioning is essential for good health. However, various factors such as genetics, lifestyle choices, and other health conditions can contribute to the development of heart disease. In this blog we will discuss different types of heart diseases and how they affect the heart and blood vessels.
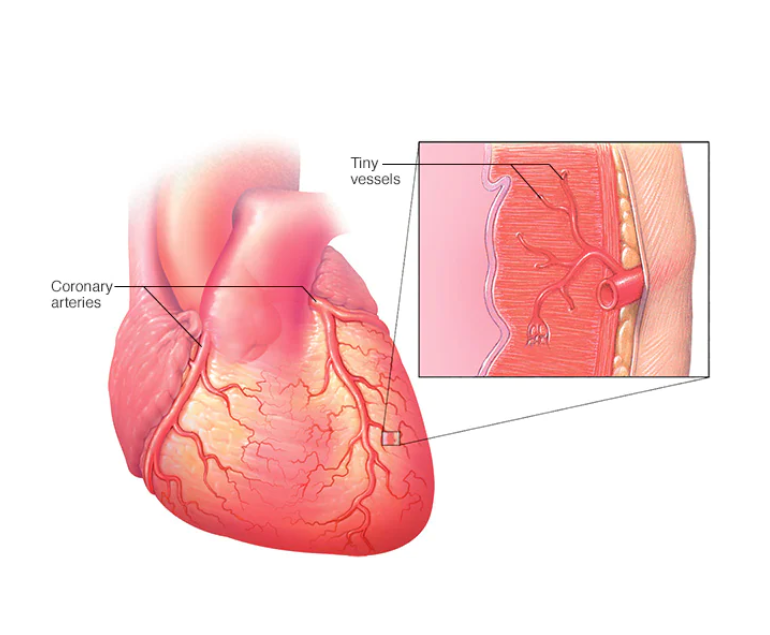
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
Coronary artery disease is a condition that occurs when the blood vessels that supply blood to the heart become narrow or blocked, causing a reduction in blood flow to the heart muscle especially when demand is high on exertion. This can lead to chest pain, angina, and heart attack. The primary cause of CAD is the build-up of plaque in the coronary arteries. Plaque is a mixture of cholesterol, fat, and other substances that can clog the arteries and make it difficult for blood to flow. The risk factors for CAD include high cholesterol, high blood pressure, smoking, obesity, and a family history of heart disease.
- Heart Attack
A heart attack, also known as myocardial infarction, occurs when a blood clot or plaque ruptures in a coronary artery, blocking blood flow to a portion of the heart muscle. This can cause damage or death to the heart muscle, which can lead to serious health problems, including heart failure. The symptoms of a heart attack include chest pain, shortness of breath, sweating, and light headedness. Quick treatment with medications and procedures such as angioplasty or bypass surgery can help prevent further damage to the heart and reduce the risk of heart failure.
- Heart Failure
During heart failure the heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the body’s requirements. This can occur due to damage to the heart muscle from a heart attack, heart valve dysfunction, myopathy, certain infections, high blood pressure, or other health conditions. Heart failure can cause a number of symptoms, including fatigue, shortness of breath, and swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet. Treatment for heart failure includes medications, lifestyle changes, and in severe cases, surgery to implant a pacemaker or defibrillator, ventricular assist devices and heart transplant.
- Arrhythmia
Arrhythmia is an irregular heartbeat that can occur due to a variety of factors, including heart disease, high blood pressure, and stress. The symptoms of arrhythmia include palpitations, dizziness, and shortness of breath. Treatment for arrhythmia may include medications, lifestyle changes, and procedures such as ablation or implantation of a pacemaker or defibrillator.
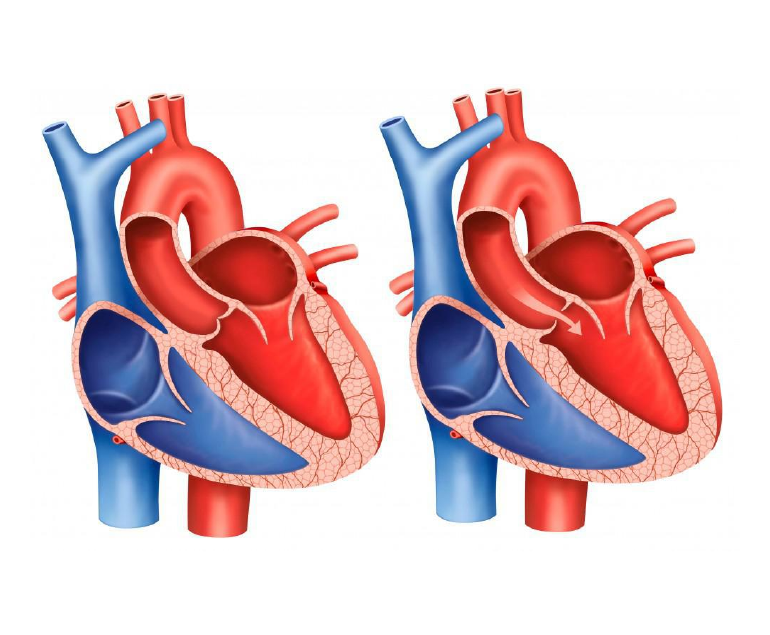
- Valvular Heart Disease
Valvular heart disease is a condition that occurs when the valves in the heart that regulate blood flow become damaged or diseased. The most common types of valvular heart disease include aortic stenosis, in which the aortic valve becomes narrow, aortic regurgitation in which the valve leaks and mitral stenosis in which mitral valve becomes narrow and mitral regurgitation, in which the mitral valve leaks. The symptoms of valvular heart disease can include chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue. Treatment may include medications, lifestyle changes, or in severe cases, surgery to repair or replace the affected valve. In selected cases percutaneous valve replacement and repair is also possible nowadays.
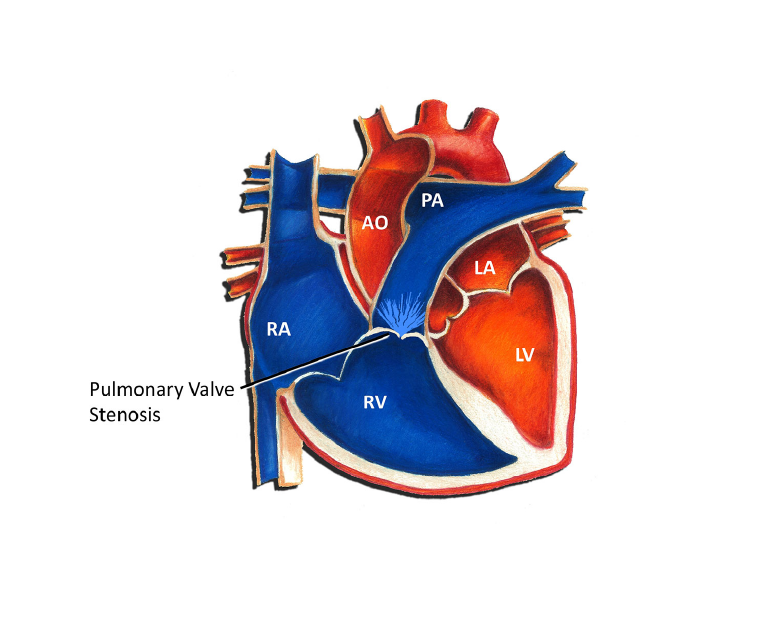
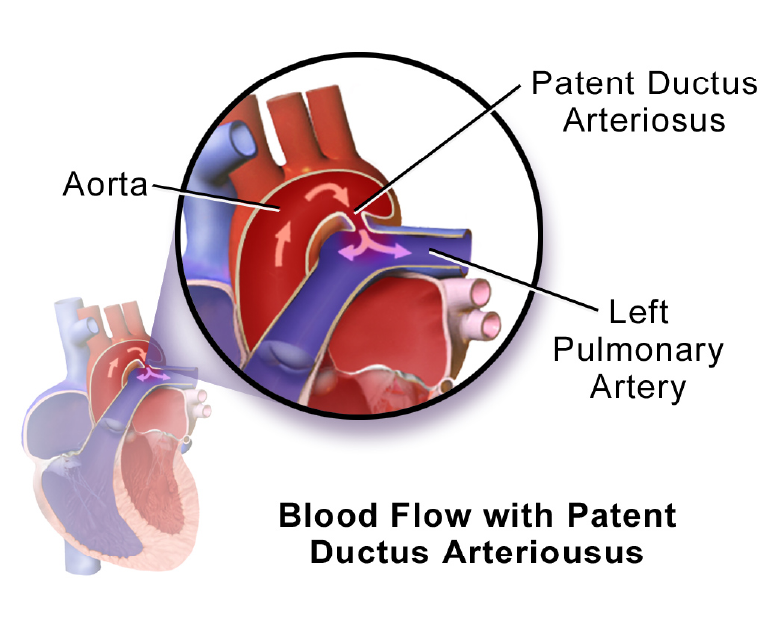
- Congenital Heart Disease
Congenital heart disease is a condition that is present at birth and affects the structure of the heart. This type of heart disease can be caused by genetic factors or environmental factors during pregnancy. The symptoms of congenital heart disease can vary depending on the specific condition, but may include shortness of breath, fatigue, and heart murmur. Treatment may include medications, lifestyle changes, or surgery to repair or replace the affected heart structures.
Conclusion
In conclusion, heart disease is a complex and often life-threatening condition that can take many forms. Understanding the different types of heart disease, their symptoms, and their causes, is an important step towards reducing the risk factors and improving the chances of maintaining good health. With timely treatment the patients can look forward to almost normal life in most cases.